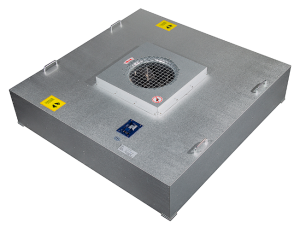
EFU (Enclosed Fan Filter Unit) Air Supply Unit
Optional DC/AC Fans
Directly Provides Clean Air Internally, Ensuring Environmental Cleanliness for Process Manufacturing
Standard Modular Design. Ultra-thin Fan, Occupying Minimal Space
Integrated Design Allows for Horizontal or Vertical Installation
Flexible Control Methods, Adjustable with Multi-position Knobs
Capable of Direct Remote Control via Computer, Either Individually or as a Group, Suitable for Large-scale Intelligent Management and Control
Low Energy Consumption, Significantly Reducing Operating Costs for Customers
Chip & Semiconductor Industry
AGF CleanCore Series Products: Providing Ultra-clean Environments for Chip Semiconductor Production
Chip & Semiconductor Industry Solution
Micro-contamination in Semiconductors Poses Severe Challenges
The manufacturing process of integrated circuits (ICs) in the semiconductor industry is complex and highly technically challenging, involving a series of crucial technological difficulties and processes that must be carried out in a constant temperature and humidity, ultra-clean environment. ICs have stringent requirements for the cleanliness of the production environment’s air. Additionally, Airborne Molecular Contaminants (AMC) have become the most significant contamination concern in IC manufacturing processes, and their effective control directly impacts product yield.
Impact of Particulate Matter:
Circuit Failures: Dust particles adhering to the wafer surface can cause short circuits and other circuit failures, impairing the functionality of the IC.
Degraded Electrical Performance: Excessive particulate matter can reduce the electrical performance of semiconductor products, such as increased haze index, and in severe cases, can even lead to product failure.
Reduced Production Cleanliness: For example, the number of particles with a diameter greater than 0.1 micrometers in one cubic meter of air cannot exceed 100.
Decreased Production Efficiency: Particulates adhering to production equipment can reduce the precision of precision production equipment, requiring frequent maintenance and upkeep.
Impact of AMC Gaseous Molecular Contaminants:
Hardening of Photoresist Surface and T-shaped Defects: AMC can cause hardening of the photoresist surface, leading to T-shaped defects.
Unwanted Chemical Reactions: Acidic gases, alkaline gases, organics, refractory organics, and dopant organics can undergo unnecessary chemical reactions with each other.
Uncontrolled Etching Rates: Dibutyl phthalate (DOP) can easily adhere to the wafer surface and form silicon carbide (SiC), making it difficult to control etching rates.
Changed Threshold Voltage: Gaseous contaminants such as boron trioxide (B2O3) and boron trifluoride (BF3) can contaminate the wafer surface.
Contaminated Wafer Surface: Pollutant gases such as HF, HCl, H3PO4, Cl2, NOx, SOx, etc., can contaminate the wafer surface, leading to decreased adhesion of metals in the metallization process.
Overall, micro-contamination in semiconductors presents significant challenges that must be addressed to ensure the quality, performance, and yield of ICs.
AGF Microelectronics Semiconductor Customized Air Filtration Solutions
The AGF CleanScience series of air filters, encompassing dust pre-filters, HEPA and ULPA filters, as well as AMC control solutions, are designed to effectively reduce the concentration of particulate and gaseous chemical contaminants within cleanrooms. And achieve dust concentrations meeting ISO Class 1 standards and control AMC concentrations below the ppb level.
Air Guard collaborates with semiconductor manufacturers to jointly promote the application of nano-efficient filters in the high-efficiency filtration of air-conditioning units in microelectronics factories. Practical applications have proven that the cleanliness of the fresh air delivered by the air-conditioning unit’s outlet is significantly improved compared to previous products. Meanwhile, the resistance has been reduced by over 20% compared to previous products, resulting in a noticeable decrease in energy consumption. This significantly extends the lifespan of the terminal filter and further reduces shutdown maintenance costs.
Our customized effective AMC gaseous contaminant treatment solutions for microelectronics semiconductor manufacturing processes have significantly lowered the incidence of product quality defects during the manufacturing process.

AGF Practical Application Solutions and Advantages
In semiconductor manufacturing environments, our products have undergone rigorous field and laboratory verification.
The verification areas include photolithography, etching, diffusion, metallization, thin-film deposition, ion implantation, measurement equipment, as well as photomask storage and wafer storage areas.
Our AMC high-adsorption products have significantly reduced the defects in process product quality caused by chemical contamination.
AGF’s boron-free filters effectively inhibit the release of boron contamination.
High-airflow nano-efficient filters achieve extremely low energy consumption, significantly reducing operational costs and energy consumption.
Low-volatility HEPA and ULPA filters significantly reduce the release of harmful gases during use.
The verification areas include photolithography, etching, diffusion, metallization, thin-film deposition, ion implantation, measurement equipment, as well as photomask storage and wafer storage areas.
Our AMC high-adsorption products have significantly reduced the defects in process product quality caused by chemical contamination.
AGF’s boron-free filters effectively inhibit the release of boron contamination.
High-airflow nano-efficient filters achieve extremely low energy consumption, significantly reducing operational costs and energy consumption.
Low-volatility HEPA and ULPA filters significantly reduce the release of harmful gases during use.

Chip & Semiconductor Industry Related Productions
EFU Air Supply Unit

FFU Air Supply Unit
FFU (Fan Filter Unit) Air Supply Unit
Optional DC/AC Fans
Directly Provides Clean Air to Cleanrooms, Widely Used in Cleanroom Applications
Standard Modular Design for Easy Installation and Mobility
Flexible Control Methods, Adjustable with Multi-position Knobs
Capable of Direct Remote Control via Computer, Either Individually or as a Group, Suitable for Large-scale Intelligent Management and Control
Low Energy Consumption, Significantly Reducing Operating Costs for Customers
Gas Adsorption V-shaped Molecular Filter
Gas Adsorption V-shaped Molecular Filter
Filter Media: Carbon-Clamped Fabric
Structure: “V”-shaped ABS with PET Outer Frame
Optimal Continuous Operating Temperature: 10-45°C
Optimal Continuous Operating Humidity: 40-90%
Primary Application: Used for the removal of various chemical odors in air-conditioning unit ventilation systems.
Features: High broad-spectrum adsorption rate, with corresponding materials selected based on the specific gas treatment requirements.

Gas Adsorption Filter without Separator
Gas Adsorption Non-Partitioned Molecular Filter
Filter Media: Carbon-Clad Fabric
Structure: Non-Partitioned Structure
Optimal Continuous Operating Temperature: 10-45°C
Optimal Continuous Operating Humidity: 40-90%
Primary Application: Suitable for the removal of gaseous contaminants in microelectronic manufacturing processes.
Features: High broad-spectrum adsorption rate, with corresponding materials selected based on the specific gas treatment requirements. The non-partitioned structure ensures efficient gas flow and adsorption.

High-Pleat Activated Carbon for Gas Adsorption
High-Concentration Pollution, High-Airflow Molecular Filter
Filter Media: Carbon-Clamped Fabric
Structure: Large Pleat Non-Partitioned Design
Optimal Continuous Operating Temperature: 10-45°C
Optimal Continuous Operating Humidity: 40-90%
Primary Application: Suitable for the removal of various chemically contaminated gases in air-conditioning unit ventilation systems.
Features: Combines both physical and molecular filtration effects, offering high airflow capacity with low resistance.

Gas Adsorption Activated Carbon Panel Filter
High-Concentration Pollution, Long-Life Molecular Filter Plate Module
Filter Media: Activated Carbon, Impregnated Activated Carbon, Impregnated Activated Alumina, etc.
Structure: Plate-type with high-weight activated carbon filling
Optimal Continuous Operating Temperature: 10-45°C
Optimal Continuous Operating Humidity: 40-90%
Primary Application: Suitable for the removal of various chemically contaminated gases in air-conditioning unit ventilation systems.
Features: High broad-spectrum adsorption rate, with corresponding materials selected based on the specific gas treatment requirements.

Gas Adsorption Activated Carbon Filter Cartridge
High-Concentration Pollution, Long-Life Molecular Filter Cartridge
Filter Media: Activated Carbon, Impregnated Activated Carbon, Impregnated Activated Alumina, etc.
Structure: Cylindrical Standard Structure
Optimal Continuous Operating Temperature: 10-45°C
Optimal Continuous Operating Humidity: 40-90%
Primary Application: Suitable for the removal of various chemically contaminated gases in air-conditioning unit ventilation systems.
Features: High broad-spectrum adsorption rate, with corresponding materials selected based on the specific gas treatment requirements.

Gas Adsorption Activated Carbon Module
High-Concentration Pollution, Long-Life Molecular Filter Module
Filter Media: Activated Carbon, Impregnated Activated Carbon, Impregnated Activated Alumina, etc.
Structure: “V”-shaped ABS, PET Frame
Optimal Continuous Operating Temperature: 10-45°C
Optimal Continuous Operating Humidity: 40-90%
Primary Application: Suitable for the removal of various chemically contaminated gases in air-conditioning unit ventilation systems.
Features: High broad-spectrum adsorption rate, with corresponding materials selected according to different gas treatments.

Multi-efficiency Pocket Filter
Filter Media: Activated Carbon Granules
Structure: Cylindrical shape, made from coconut shell carbon, coal-based carbon, etc.
Optimal Continuous Operating Temperature: 10-45°C
Optimal Continuous Operating Humidity: 40-90%
Primary Application: Suitable for the removal of various chemically contaminated gases in air-conditioning unit ventilation systems, with a high broad-spectrum adsorption rate.

Panel Filter without Separator
Filtration Grade: E10~U16
Filter Media: Low-Boron Ultra-Fine Glass Fiber Material
Structure: Pleated Panel Design without Partitions
Continuous Operating Temperature: ≤68°C
Recommended Final Resistance: ≤350 Pa
Primary Application: Suitable for the final air supply in cleanrooms of air conditioning systems.
Features: High efficiency, low resistance, and long service life. The low-boron ultra-fine glass fiber material ensures particulate removal efficiency >99.99995% at MPPS (Most Penetrating Particle Size).

Previous
Next
